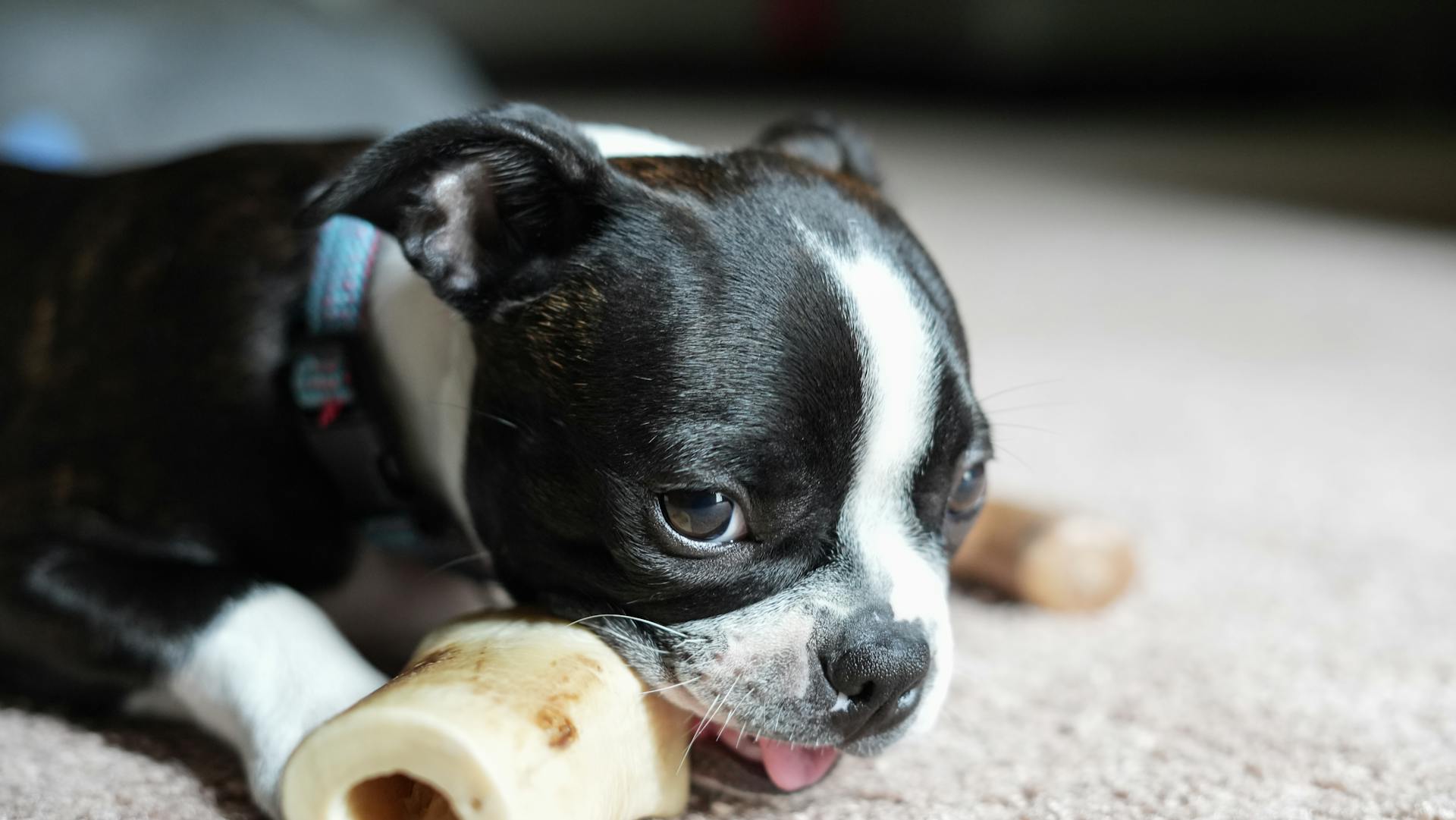
There are a number of reasons why dogs chew bones on their owners. It could be that the dog is teething and is trying to relieve the discomfort by chewing on something hard. It could also be that the dog is bored and is looking for something to do. Additionally, some dogs may chew bones as a way of showing affection to their owners.
Whatever the reason, it is important to remember that bones are not toys and should not be given to dogs to chew on unsupervised. Chewing on bones can be dangerous for dogs as they can splinter and cause choking or gastrointestinal blockages. If you think your dog is chewing on bones out of boredom, try providing them with more stimulating toys or puzzles to keep them occupied. If the chewing is due to teething, give your dog a frozen washcloth or ice cube to chew on instead of a bone.
Is it because he's anxious?
It is because he is anxious. Anxiety is a feeling of worry, nervousness, or unease about something with an uncertain outcome. Anxiety disorders are a type of mental disorder and can cause significant impairment in daily life. It is because he is anxious that he feels like he needs to control everything. He is afraid of what might happen if he can't control it. He is anxious about the future and feels like he needs to plan for every possible outcome. He is anxious about what other people think of him and how they will judge him. He is anxious about making mistakes and not being perfect.
Consider reading: Grooming a Nervous Dog
Is it because he's teething?
When our son started getting fussy and waking up more at night, my husband and I started asking ourselves, “Is it because he’s teething?” We had read that teething can be a difficult time for babies and their parents, so we decided to do some research on the subject.
According to WebMD, teething is the process whereby an infant’s first teeth erupt through the gums. This can occur any time between 4-7 months of age, but most babies will get their first teeth around 6 months. While some babies sail through this process with no problems, others can experience discomfort and pain.
There are a few signs that may indicate that your baby is teething, including capriciousness, waking up more at night, drooling, chewing on everything, and putting their fingers in their mouth. If your baby is displaying any of these symptoms, it’s likely that they are teething.
So, how can you help your baby through this difficult time? There are a few things you can do to make their teething experience more comfortable.
First, offer them something to chew on. teething rings and toys can help relieve pressure on the gums and provide distraction from the discomfort. You can also try cold foods such as frozen bananas or yoghurt.
Secondly, use a teething gel to numb the gums and provide relief. There are a number of brands available, just make sure to read the label and only use a small amount.
Finally, try to remain calm and patient. Teething can be a trying time for both you and your baby, but it will eventually come to an end. In the meantime, do your best to comfort and support them through this difficult phase.
Related reading: Dog Boarding for Difficult Dogs
Is it because he likes the taste of the bone?
There are a number of reasons why Rover might like the taste of the bone. It could be that he simply enjoys the flavor or that he finds it satisfying. Alternatively, it could be that the bone provides him with some nutritional benefits that he otherwise would not get from his diet.
Rover is not the only animal that enjoys the taste of bone. In fact, many animals, including humans, find bone to be a delicious treat. This is likely because bone is rich in nutrients, including protein, fat, and minerals.
So, why does Rover like the taste of bone? It could be for any number of reasons. However, one thing is for sure: it's not because he's trying to be like his canine companions!
Suggestion: Why Does My Dog Want to Attack Other Dogs
What can I do to stop my dog from chewing his bone on me?
There are a few things you can do to stop your dog from chewing his bone on you. The first is to make sure that you are providing him with plenty of chew toys and bones of his own. This will help to redirect his chewing urges away from you and onto something that is specifically meant for him to chew on. You can also try training your dog with positive reinforcement - rewarding him whenever he chews on his toys instead of you. Finally, if your dog is already used to chewing on you, you may need to be more forceful in your corrective measures. This could involve saying "no" in a firm voice, spraying him with water, or giving him a short time-out in his crate.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the difference between feeling anxious and having an anxiety disorder?
There is a big difference. One person might feel anxious from time to time, but not have an anxiety disorder. An anxiety disorder is diagnosed when the person experiences frequent, overwhelming anxiety that negatively impacts their life.
Why is my child so anxious all the time?
The most common reasons for anxiety in kids vary from child to child, but can include: reacting strongly to situations that cause fear and anxiety in other kids (such as travelling, being around big groups of people, or jumping from high places); having low self-esteem because of worries about appearance, size, or ability; experiencing problems at home or at school that make them feel overwhelmed, like not getting on with friends or being made fun of; being closely watched by parents or carers who are trying to screen out risks before they become too serious; and a history of trauma such as abuse or loss.
What is abnormal anxiety?
People who experience abnormal anxiety may worry excessively about many different things, even if there is no reason to be anxious. They may feel tense and uncomfortable even when there’s no reason to be, and they often find it difficult to relax. These symptoms can severely impact daily life and prevent people from carrying out their usual activities.
Is it normal to be anxious about math tests?
There’s no one answer to this question, as everyone experiences anxiety in different ways. However, if you feel intense anxiety or fear around math tests or any other type of academic challenge, it may be a sign that you have an anxiety disorder. If this is the case for you, talk to your doctor or therapist about how you can manage your symptoms.
What is the difference between stress and anxiety?
Stress is simply a reaction to a demanding situation. It's how we handle the demands of life. Anxiety, on the other hand, is an illness characterised by intense fear or worry that reaches a level that significantly interferes with normal daily activities.
Sources
- https://www.quora.com/What-are-the-signs-that-my-crush-is-trying-to-get-my-attention
- https://www.independent.ie/life/family/mothers-babies/is-teething-just-a-myth-31458063.html
- https://allanimalsfaq.com/dog/why-does-my-dog-chew-his-toys-on-me/
- https://www.quora.com/A-guy-rejected-me-but-why-does-he-still-want-my-attention
- https://allanimalsfaq.com/dog/why-does-my-dog-chew-his-bone-on-me/
- https://wollongongmums.com.au/is-it-because-he-is-teething/
- https://thedogkeepers.com/why-does-my-dog-chew-his-bone-on-me/
- https://www.understood.org/en/articles/anxious-vs-anxiety
- https://www.goodtherapy.org/blog/is-she-more-anxious-than-he-is-probably-heres-why-0912174
- https://understandingthegospel.org/blogs/paul-coxall/is-it-okay-to-be-anxious/
- https://www.oodlelife.com/why-does-my-dog-chew-his-toys-on-me/
- https://www.quora.com/Is-it-true-that-when-a-person-is-anxious-its-because-theyre-thinking-about-the-future-and-when-a-person-is-sad-its-because-theyre-thinking-about-the-past-How-can-one-be-focused-on-being-in-the-present
- https://mishpacha.com/can-i-be-calm-if-hes-anxious/
- https://www.girlsaskguys.com/guys-behavior/q4570293-why-is-he-trying-to-get-my-attention
- https://ideapod.com/signs-he-wants-you-to-notice-him/
Featured Images: pexels.com